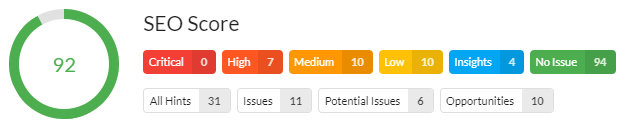
SEO
Search Traffic
Traffic from organic search is like the ultimate truth when it comes to SEO. After all, rankings mean nothing if they don’t drive relevant traffic and conversions.
So it can be worthwhile to investigate any potential issues that exist within the search traffic data. Why ‘can’ be worthwhile’ vs ‘worthwhile?’
Because there is some element of subjectivity, a wrong signal on one site might represent a good signal on another site.
Bounce rate offers a classic example. You could have a page that ranks for ‘what is the weather today in Australia’, which would have an extremely high bounce rate.
A Visitor comes on the page, gets the answer, bounces away, and this would not be considered a problem.
But if you have a 1500 word blog post on an eCommerce site that ranks as ‘best kayak for white water rivers,’ you would be alarmed/disappointed if the bounce rate was high.
Internal – Link structure, Improper Code Use, URL Upper Case Letter, URL White Space
The Internal Hints cover various issues in terms of URL paths and how URLs resolve, which can impact both users and search engines.
Identifying systemic issues with internal URLs can help you better understand the website and what may be holding it back. Identifying patterns in the URL paths can also be given you a better understanding of the site’s underlying structure and find areas to drill down into further.
Links – Broken, Good, Orphaned, White Space
Links are fundamental to how the internet works by creating connections between all the disparate documents on the web. Internal links are connections between pages on the same website, and internal linking can significantly impact the ranking ability of a given URL.
Indexability – Index, No Index, Canonical, Crawlable, Not Found
Indexability relates to the technical configuration of URLs so that they are either Indexable or Not Indexable.
Search engines generally take the stance that any successful URLs (i.e. HTTP status 200) they find should be indexed by default – and they will, in the main, index everything they can find. However, you can give specific signals and directives to search engines that instruct them to NOT index particular URLs.
Redirects – Broken, Depth, HTTP, HTTPS
Redirects are an entirely necessary element of website management, to the point where it is extremely rare that you audit a website that has no redirects at all.
From a user perspective, redirects are generally not that bad, assuming the user ends up on the correct destination page eventually. But they do add some additional time when loading the page, which is not a good thing, and when you end up with big chains of redirects it is most definitely a bad thing.
From a search engine perspective, internal redirects are sub-optimal. They force the crawler to request additional pages, which essentially means it has to work harder. If it has to do extra work following redirects in order to access certain pages, it may use up your website’s allocated crawl budget before it has finished crawling all your pages.
On-Page – Readability, Sentiment, Title, Header 1, Meta Descriptions
On-Page is one of the most fundamental facets of SEO, and is basically considered table stakes – you need to be getting the basics right if you expect to compete in competitive spaces. On-Page SEO remains one of the main methods for communicating to search engines the subject matter of a given URL. There are a number of fundamental elements that need to be handled correctly, for maximum benefit.
Most modern CMS platforms allow you to control and adjust all the major On-Page SEO elements, so making fixes or amendments is achievable for SEOs of basically any level.
The on page fundamentals are typically the page <title>, the meta description and the <h1> tag.
Duplicate Content – Title, Header, Page, Canonical, Blog
Duplicate content on your website is something that search engines have pushed back against, to the point where it is taken very seriously by SEOs. Duplicate content is problematic for search engines, in the sense that they don’t want to serve duplicate results to searchers.
If you have 2 different URLs that contain identical content, search engines typically will only wish to serve one of these URLs as a search result for a given query. If you have 2 URLs that have different body content, but identical h1 and title tag, search engines may be confused as to which one is the most suitable option to include in search results for a given query.
This can result in these URLs effectively competing with each other for the same query, and potentially hurting each other’s ability to rank (this is known as keyword cannibalization).
Sitemaps – Redirects, Missing, Not Found, Error, No Index
An XML Sitemap is an extremely useful tool in an SEO’s arsenal. It allows you to unambiguously declare exactly which URLs you wish to be indexed on a website.
And these are also the only URLs an XML Sitemap should contain – only the URLs you actually want to be indexed.
As a minimum, these must be URLs that return a 200 status code and are indexable. As such, the XML Sitemap Hints serve to highlight instances where this is not the case.
Response vs Render – Problems in Different Browsers
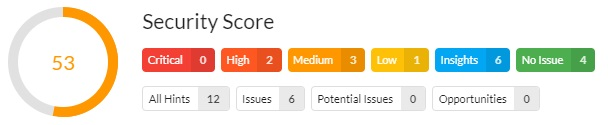
Security
Website security is becoming an increasingly important topic, as more individuals, businesses and governing bodies are becoming concerned with the risk to personal data posed by inadequate web security practices.
Risks of Private Data Exposure – Server Encryption, Code Injections, Content Delivery Networks, Mixed HTTP/HTTPS Content
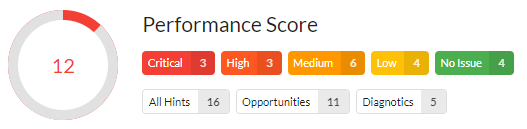
Performance
Improving page performance has been an important aspect of website optimization for many years.
Google told us over a decade ago that they use site speed in their search rankings:
“Speeding up websites is important — not just to site owners, but to all Internet users. Faster sites create happy users and we’ve seen in our internal studies that when a site responds slowly, visitors spend less time there.”
Google
And there are about a million studies online about improving engagement/conversion with improved page speed:
Ranking Related, Paid Search Related. Poor Scores Cost You Money
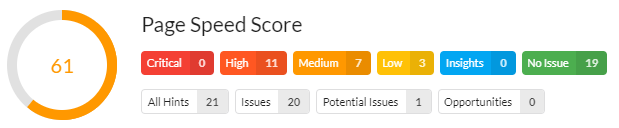
As development techniques have advanced, and website owners are trying to do more with their websites, page speed has become an ever more important factor.
‘Performance’ itself has merged into a usability consideration, to the extent that Google now considers page performance worthy of being rolled into their page experience signals, and used to help determine the order of search results.
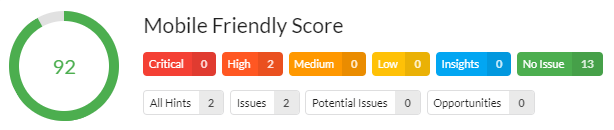
Mobile
Having a mobile-friendly website is a big deal, to the point where it is at least as important – if not more important – to have a website that works well as well on mobile as it does on desktop.
As the penalties for not having a mobile-friendly website can be harsh – from users abandoning early to depressed search engine rankings – all professional digital marketers are in complete agreement that a mobile-friendly website is table stakes.
AMP
AMP is an open-source library that is designed to produce fast-loading pages that are optimized for mobile. For certain mobile search queries, Google will serve pages directly from the Google AMP cache
The most common example you will see in the wild is AMP pages used for news stories, which appear in an AMP carousel box above the traditional search results. You can see the AMP ⚡ symbol in the top right-hand corner, and clicking through to any of these results will take you to the cached AMP page on Google’s servers
Page Resources
Images, Code, PDFs – Poorly Executed Can Cause Performance and Index Issues
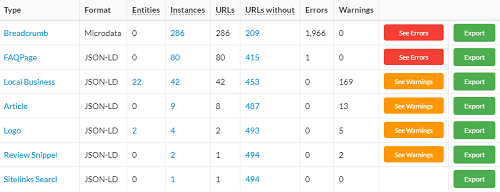
Structured Data | Schema
Schema is now an integral element of SEO. From a practical perspective, structured data is a way to give meaning to your web page content, using a format that computers can understand.
The Schema.org vocabulary currently consists of over 800 types and is growing all the time, yet Google only supports ~20. Although a large proportion of these types will never be relevant for SEO, it does give an idea of the potential for growth in this area.
Google has a nasty habit of quietly making little changes that suddenly mean your structured data doesn’t meet their criteria anymore.
External
Links out from your website to other websites. These links should reflect the content on the page or the overall website. Links should go to authoritative websites, government agencies or industry regulators and suppliers. Websites regularly remove or change the location of topical content you have linked from your website. Recognizing the removal or change and adjusting your links or content is important in maintaining Expertise, Authority and Trust (EAT) a cornerstone for ranking well in Google search results.
Strategy & Management For Customized Legal Marketing Campaigns
Give the team at Exemplar Digital Marketing a call at 1.250.507.2332 to find out how we can help you.
